RxJava 共有三个大版本:
-
Version 1.x
The 1.x version is end-of-life as of March 31, 2018. No further development, support, maintenance, PRs and updates will happen. The Javadoc of the very last version, 1.3.8, will remain accessible.
-
Version 2.x
The 2.x version is end-of-life as of February 28, 2021. No further development, support, maintenance, PRs and updates will happen. The Javadoc of the very last version, 2.2.21, will remain accessible.
-
Version 3.x (Javadoc)
- Single dependency: Reactive-Streams.
- Java 8+ or Android API 21+ required.
- Java 8 lambda-friendly API.
- Android desugar friendly.
- Fixed API mistakes and many limits of RxJava 2.
- Intended to be a replacement for RxJava 2 with relatively few binary incompatible changes.
- Non-opinionated about the source of concurrency (threads, pools, event loops, fibers, actors, etc.).
- Async or synchronous execution.
- Virtual time and schedulers for parameterized concurrency.
- Test and diagnostic support via test schedulers, test consumers and plugin hooks.
- Interop with newer JDK versions via 3rd party libraries, such as
- Java 9 Flow API
- Java 21 Virtual Threads
- Learn more about RxJava in general on the Wiki Home.
1. RxJava 基础
io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable: 0..N flows, supporting Reactive-Streams and backpressureio.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Observable: 0..N flows, no backpressure,io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Single: a flow of exactly 1 item or an error,io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Completable: a flow without items but only a completion or error signal,io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Maybe: a flow with no items, exactly one item or an error.
1.1 Observable
Observable 是 Rx 中的核心抽象,代表一个可观察的对象。其产生数据流,并可以结合各种操作符来改变数据流。
常用的创建 Observable 方法有两种:
- 使用 fromXxx(), just() 等方法从现有对象中创建;
- 使用 Observable#create() 来自定义数据流;
|
|
create() 方法的参数为 ObservableOnSubscribe 类型,是一个以 Emitter 为参数的函数。当有订阅者订阅 Observable 时,ObservableOnSubscribe 表示的方法便会执行一次,以产生数据。
考虑到在 ObservableOnSubscribe 中,如上 c.onNext("hello"), 便是直接调用订阅者的回调事件,这是同步调用的。所以得出结论:观察者的监听方法调用是由数据发送的那个线程执行。
|
|
1.2 Observer
Observer 观察者,通过实现三个方法来响应 Observable 数据流
- onNext(data) 处理数据
- onError(error) 处理异常,然后中断流
- onComplete() 标记流的完成
2. Observable 的几个特点
每次订阅时,create 方法都会执行一遍,特殊情况下会有问题,如使用 http 访问远程数据时,每个观察者都会创建自己独立的 http 客户端,这会导致资源浪费。
Subject 可以解决这个问题,Subject 同时实现了 Observable 和 Observer 接口,即是观察者,又是一个可观察对象。Subject 会维护一个观察者列表。 通过引用 Subject,然后订阅真正的数据源,把自身当作一个中介,把上游的数据源发布到下游。
介绍几种 Subject
-
PublishSubject,实时的把上游收到的数据,转发到全部的订阅者。

-
BehaviorSubject, 保留最近的一个数据给新观察者,后接收的数据实时转发到订阅者

-
ReplaySubject, 重复所有历史数据给新观察者,
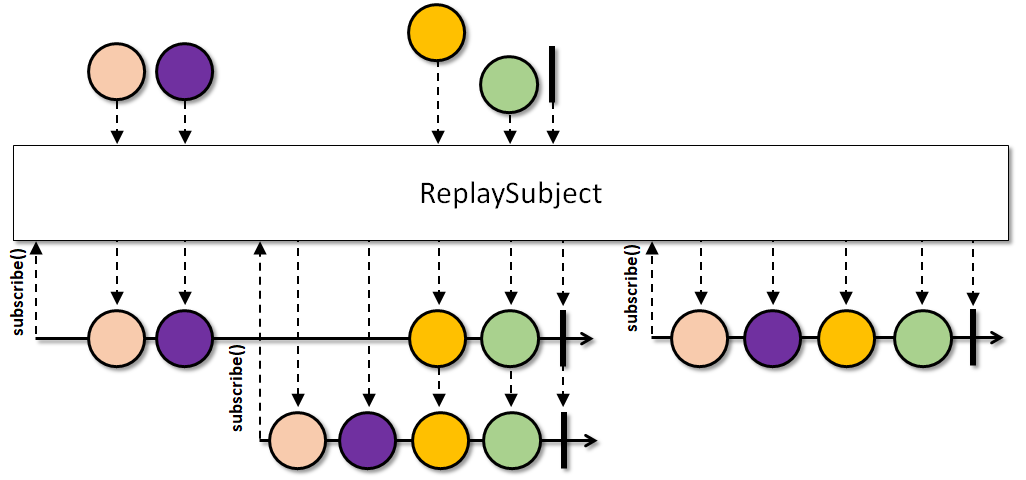
-
AsyncSubject, 当上游数据完成时,取最后一个转发给订阅者

3. 操作符
Creating
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Create | create an Observable from scratch by calling observer methods programmatically |
| Defer | do not create the Observable until the observer subscribes, and create a fresh Observable for each observer |
| Empty | create Observables that have very precise and limited behavior |
| From | convert some other object or data structure into an Observable |
| Interval | create an Observable that emits a sequence of integers spaced by a particular time interval |
| Just | convert an object or a set of objects into an Observable that emits that or those objects |
| Range | create an Observable that emits a range of sequential integers |
| Repeat | create an Observable that emits a particular item or sequence of items repeatedly |
| Start | create an Observable that emits the return value of a function |
| Timer | create an Observable that emits a single item after a given delay |
Transforming
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Buffer | periodically gather items from an Observable into bundles and emit these bundles rather than emitting the items one at a time |
| FlatMap | transform the items emitted by an Observable into Observables, then flatten the emissions from those into a single Observable |
| GroupBy | divide an Observable into a set of Observables that each emit a different group of items from the original Observable, organized by key |
| Map | transform the items emitted by an Observable by applying a function to each item |
| Scan | apply a function to each item emitted by an Observable, sequentially, and emit each successive value |
| Window | periodically subdivide items from an Observable into Observable windows and emit these windows rather than emitting the items one at a time |
flatMap 的特性:
flatMap() 将 Observable 中的每个元素转换为另一种 Observable 流,flatMap 不保证转换后流的顺序跟原始顺序一致。flatMap 内部使用了 merge 操作 符,它同时订阅所有的子 Observable,对他们不做任何区分。因为它是异步的,多线程式的进行转换,可用用参数控制并发数量。
如需要保证顺序,可使用 concatMap, 他类似 flatMap,但可用包装原始元素的顺序和转换后的 Observable 流的顺序一致
Window 和 Buffer 的区别
Window 同 Buffer 都可以依据时间段或指定数据量来收集一段数据,两者不同之处在于 Window 生成的是 Observable 流,而 Buffer 生成的列表。
Filtering
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Debounce | only emit an item from an Observable if a particular timespan has passed without it emitting another item |
| Distinct | suppress duplicate items emitted by an Observable |
| ElementAt | emit only item n emitted by an Observable |
| Filter | emit only those items from an Observable that pass a predicate test |
| First | emit only the first item, or the first item that meets a condition, from an Observable |
| IgnoreElements | do not emit any items from an Observable but mirror its termination notification |
| Last | emit only the last item emitted by an Observable |
| Sample | emit the most recent item emitted by an Observable within periodic time intervals |
| Skip | suppress the first n items emitted by an Observable |
| SkipLast | suppress the last n items emitted by an Observable |
| Take | emit only the first n items emitted by an Observable |
| TakeLast | emit only the last n items emitted by an Observable |
Combining
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| And/Then/When | combine sets of items emitted by two or more Observables by means of Pattern and Plan intermediaries |
| CombineLatest | when an item is emitted by either of two Observables, combine the latest item emitted by each Observable via a specified function and emit items based on the results of this function |
| Join | combine items emitted by two Observables whenever an item from one Observable is emitted during a time window defined according to an item emitted by the other Observable |
| Merge | combine multiple Observables into one by merging their emissions |
| StartWith | emit a specified sequence of items before beginning to emit the items from the source Observable |
| Switch | convert an Observable that emits Observables into a single Observable that emits the items emitted by the most-recently-emitted of those Observables |
| Zip | combine the emissions of multiple Observables together via a specified function and emit single items for each combination based on the results of this function |
| Concat | emit the emissions from two or more Observables without interleaving them |
zip() 或 zipWith(), 两个流的元素进行结合成一对。注意,由于 zip 的结合一定要两个元素,这在两个流的速度大致一致时有良好的表现,但流速不一致时,较快的流将会等待较慢的流
可用静态方法 combineLatest() 或对象方法 withLatest() 解决 zip 的缺陷,两个不同速度的流,都会结合最近的另一个流元素,没有结合元素的将会被丢弃
Error Handling
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Catch | recover from an onError notification by continuing the sequence without error |
| Retry | if a source Observable sends an onError notification, resubscribe to it in the hopes that it will complete without error |
Utility
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Delay | shift the emissions from an Observable forward in time by a particular amount |
| Do | register an action to take upon a variety of Observable lifecycle events |
| Materialize/ Dematerialize | represent both the items emitted and the notifications sent as emitted items, or reverse this process |
| ObserveOn | specify the scheduler on which an observer will observe this Observable |
| Serialize | force an Observable to make serialized calls and to be well-behaved |
| Subscribe | operate upon the emissions and notifications from an Observable |
| SubscribeOn | specify the scheduler an Observable should use when it is subscribed to |
| TimeInterval | convert an Observable that emits items into one that emits indications of the amount of time elapsed between those emissions |
| Timeout | mirror the source Observable, but issue an error notification if a particular period of time elapses without any emitted items |
| Timestamp | attach a timestamp to each item emitted by an Observable |
| Using | create a disposable resource that has the same lifespan as the Observable |
ObserveOn 和 SubscribeOn 的区别:
ObserveOn 将指定下游操作符运行在哪个线程上,整个流程涉及两个线程,造成了 ObserveOn 的上游是同步的,但下游从主线程看是异步的
SubscribeOn 是将整个流运行在其他线程上,而不是 Observable.create() 的线程, 由于只涉及一个线程,所以整体流程还是同步的。多次调用 SubscribeOn 只有最上游的生效。
Conditional and Boolean
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| All | determine whether all items emitted by an Observable meet some criteria |
| Amb | given two or more source Observables, emit all of the items from only the first of these Observables to emit an item |
| Contains | determine whether an Observable emits a particular item or not |
| DefaultIfEmpty | emit items from the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable emits nothing |
| SequenceEqual | determine whether two Observables emit the same sequence of items |
| SkipUntil | discard items emitted by an Observable until a second Observable emits an item |
| SkipWhile | discard items emitted by an Observable until a specified condition becomes false |
| TakeUntil | discard items emitted by an Observable after a second Observable emits an item or terminates |
| TakeWhile | discard items emitted by an Observable after a specified condition becomes false |
Mathematical and Aggregate
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Average | calculates the average of numbers emitted by an Observable and emits this average |
| Count | count the number of items emitted by the source Observable and emit only this value |
| Max | determine, and emit, the maximum-valued item emitted by an Observable |
| Min | determine, and emit, the minimum-valued item emitted by an Observable |
| Reduce | apply a function to each item emitted by an Observable, sequentially, and emit the final value |
| Sum | calculate the sum of numbers emitted by an Observable and emit this sum |
Connectable Observable
| Operator | Note |
|---|---|
| Connect | instruct a connectable Observable to begin emitting items to its subscribers |
| Publish | convert an ordinary Observable into a connectable Observable |
| RefCount | make a Connectable Observable behave like an ordinary Observable |
| Replay | ensure that all observers see the same sequence of emitted items, even if they subscribe after the Observable has begun emitting items |
4. 背压 Backpressure
rxjava 中,可以通过使用 buffer, window 等操作符来缓存部分数据,已达到批量处理操作,抵御数据洪峰。但真正灵活的还是背压功能,因为只有消费者自己知道自己的消费速度。
背压,意思为当消费者的消费速度跟不上生产者的生产速度时,消费端提供一种反馈通道来通知生产者调整发射速度
Flowable 类似于 Observalbe,但支持 backpressure 功能
|
|
通过实现 DefaultSubscriber 的 onStart 方法,在 onStart 中使用 request 初始化消费数量(默认 Long.MAX_VLAUE),然后在每次 onNext 中在使用 request 请求获取消息(这样把本是 push 模型的 rxjava 变成了 pull 模型)
rxjava 中 Flowable 创建的源都支持背压操作。但如果想自定义源,需要自己实现背压支持,需要在 Flowable 的 Emitter 支持 requested() 方法,可以知道下游所设定的 request 值。
下列我们创建一个可持续发送数据的源,并使用 requested 和 request 方法来自定义背压操作
|
|